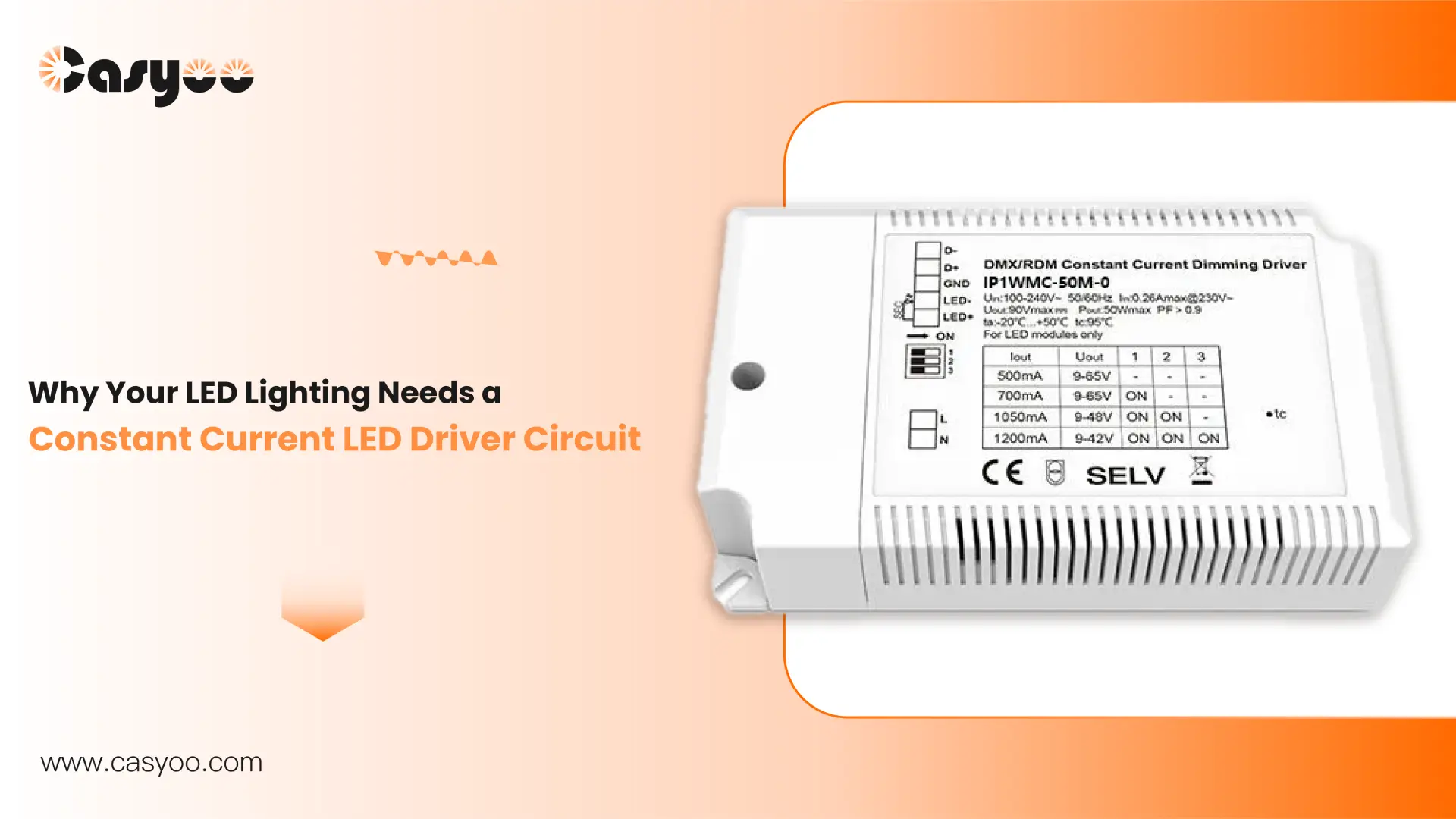
Ever wondered what keeps your LED lights shining consistently? It’s the LED driver, the essential component that ensures stable, precise current for optimum performance. Without a constant current driver circuit, LEDs can flicker, dim, or fail prematurely.
In this article, we take a review of the basic functions, working principle, and necessary considerations in choosing a suitable constant current LED driver for your lighting systems. It can be useful for everyone to understand how these drivers work to keep LEDs running reliably and effectively for years.
Function and Basics of Constant Current LED Drivers
Why Is Constant Current Required for LEDs?
Unlike other lighting technologies, LEDs are sensitive to changes in voltage. Changes in current can cause an LED to overheat, lose brightness, or even fail prematurely. A constant current driver acts to stabilize this by regulating the current to the requirements of the LED. This helps it operate optimally over its life span. For example, when an LED is driven with too much current, it will burn out very quickly. When an LED is driven with too little current, it may also behave erratically and may not light up brightly.
Working Principle of Constant Current LED Drivers
This is realized by the constant current drivers through an adjustment of the output voltage, which keeps the current constant. The driver has feedback mechanisms, sensing the output current and adjusting accordingly. when the resistance of the LED changes with temperature variation, the driver adjust the output voltage to keep the current constant. In other words, dynamic adjustment ensures the LED operates within its safe current range. This prevents damage caused by power fluctuations.
Types and Variations of LED Drivers
Constant Current vs. Constant Voltage LED Drivers
A constant voltage driver and a constant current driver differ primarily in how power is regulated. A constant current driver will deliver constant current to the LED, whereas a constant voltage driver will deliver constant voltage. Constant voltage drivers are commonly used with LED strips and similar applications with standardized voltage. However, constant current drivers are necessary for individual LEDs or LED arrays. This makes constant current drivers a must for most lighting designs, especially in commercial and industrial applications.
Dimmable vs. Non-Dimmable Constant Current LED Drivers
The dimming feature is one of the most popular properties in most contemporary lighting systems. Dimmable constant current LED drivers allow brightness adjustments. They are ideal for places where dimming is needed, such as offices, theaters, and homes. Normally, these drivers apply either Triac dimming, 0-10V dimming, or PWM control for changing the light output. While on the other hand, non-dimmable drivers have a fixed output and are used in those applications where there is no need for dimming.
PWM vs. Constant Current Drivers
Constant current drivers are commonly used for powering LEDs. However, PWM drivers are widely used to control light intensity by rapidly switching the current on and off. This has been in place for the dimming of LEDs or managing brightness levels in a more energy-efficient way. However, sometimes PWM dimming results in flicker, especially when the switching frequency is not high enough. Conversely, constant current drivers control the output current and are more appropriate for flicker-free, steady brightness.
Designing and Selecting Constant Current LED Drivers
How to Choose the Right Constant Current LED Driver?
Choosing the right constant current LED driver is one of the major decisions in the performance and reliability of a lighting system. Among the critical factors to be put into consideration are the current rating, voltage range, and power requirements of the LED. For proper performance, the driver must be compatible with the operating voltage and current specifications of the LEDs. In order to reduce heat production and energy consumption, it should also have a high power efficiency. Proper driver will make the whole system efficient and can last longer.
Calculation of LED Current and Driver Requirements
It is also important that the right current and driver are selected so the LED is operated within its optimal range. The LED’s forward voltage and the intended power output must be known in order to calculate the required current. The formula for calculating current is:
Current (A) = Power (W) / Voltage (V)
Having plugged in the current you need, pick a driver that will satisfy both the current and voltage requirements. You can also use tools and calculators to simplify this step and ensure that the selected driver is delivering the appropriate power efficiently.
Wiring and Connection of Constant Current LED Drivers
How Can an LED Driver with Constant Current Be Wired?
Wiring a constant current LED driver properly is very important so that the LED can be operated within the specified parameters. Most series configurations connect the driver in series with the LED or array of LEDs. In the series circuit, the current remains constant across the whole circuit, which is ideal for a constant current driver. The number of LEDs in the series will affect the voltage. It is very important to make sure the total forward voltage of the LEDs will match the output voltage of the driver, so as not to have overvoltage or undervoltage.
When wiring a constant current LED driver, the general steps are:
- Voltage and current ratings: Make that the driver’s output satisfies the LED’s voltage and current specifications.
- Attach the driver’s anode side to the LED’s anode side.
- The driver’s negative terminal should be connected to the LED’s negative terminal.
- Provide adequate heat sinking:You need to manage the thermal conditions by mounting the driver in a location with good airflow. If possible, solder a heatsink onto the driver to prevent overheating.
Incorrect wiring can also result in inefficient operation, a possible failure of drivers, or even the LED themselves.
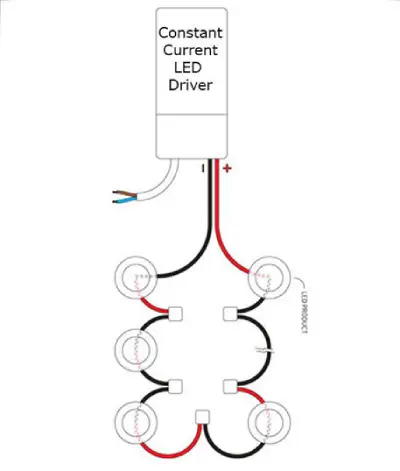
Connecting Multiple LED Drivers: Series vs. Parallel Wiring
The type of LED driver being used determines whether to use a series or parallel wiring scheme when connecting several LEDs. LED drivers with constant current are often connected in series. This way, it guarantees that each LED will have the exact same current flowing through it, which is important to maintain consistent performance.
In a series connection, the voltage is shared by all LEDs, but the current flows uniformly through each one. This is crucial when using LEDs with variable voltages. Although the current remains constant, the driver adjusts the voltage based on the total voltage of the series string.
In contrast, a parallel connection requires a constant voltage driver. Each branch needs the same voltage, but currents may vary, depending on the number of LEDs in the branch. Generally, a series connection is preferred for constant current drivers, as it ensures proper current regulation for each LED.
How to Test a Constant Current LED Driver?
Testing a constant current LED driver involves checking both the current and the voltage to ensure they are as specified by the LED. To conduct a basic test:
- Measure the output voltage: Using a multimeter, the voltage between the driver’s output terminals should be measured and compared to the expected voltage value for the LED configuration.
- Measure the output current: Using a clamp meter, measure the current being output by the driver. It must be equal to the rated current of the LED.
- Stability check: Monitor the driver output over some time to ensure that the current is stable with no oscillations.
You might have to carry out these tests in order to be able to trace errors such as wrong output or unstable current and be in a position to correct them before they damage the LED or reduce the performance of the lighting system.
Troubleshooting Constant Current LED Drivers
While constant current LED drivers are pretty reliable, they can still fail over time due to lack of maintenance or extended exposure to environmental conditions that may cause malfunction. The most common types of failures include:
Flicker:It may occur when the current is not stable or in case the driver is not compatible with the specification of the LED itself. It can also be due to exterior causes, for example, that might come from power supply quality or compatibility in dimming features.
- Solution: Check that the driver is paired correctly to the LED, check for bad connections, and if dimming is an issue then look at drivers with better quality dimming function.
Overheating:Overheating can lead to driver failure and reduced LED lifespan. This is often caused by poor thermal management or a mismatch between the driver and the LED’s power requirements.
- Solution: Ensure adequate heatsinking via heatsinks or active cooling solutions and that the driver is rated for the power load being demanded.
Driver Failure:If the failure of the LED driver is complete, it could be due to poor quality components or incorrect wiring or excessive environmental stress (for example, extreme temperatures).
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and input voltage specs, then replace the driver with a higher power-rated one if necessary.
Take Action: Ensure Your LED Lighting Systems Are Powered by the Best
Are your LED drivers optimized for maximal performance? The right constant current LED drivers can help you raise efficiency, extend the life of your lighting, and also save on energy costs. Now is the time to review your current system and consider upgrading to the most reliable, energy-efficient solutions available.
Bring your lighting systems to the next level: contact us today to find out how our state-of-the-art LED drivers can meet your requirements. To ensure that your lights continue to function at their best for many years to come, let our knowledgeable staff assist you in finding the ideal match for your project.