Luminous efficacy is an important indicator to measure the energy conversion efficiency of light sources. Therefore, before choosing among different lights, you need to learn about this concept. How to measure luminous efficacy? What are the relations between luminous efficacy, luminous efficiency, lumen, and watt? Which kind of lamps have the highest luminous efficacy? Read this passage where we introduce all about luminous efficacy!
How do you calculate luminous efficacy?
Electrical energy is converted into heat and light in a lamp. To know the efficacy of a lamp in converting electrical energy into useful light, we use the ratio of light energy to electrical energy, that is, the luminous efficacy. Electrical energy is measured in power (watts), while light energy is measured in luminous flux (lumens). Luminous efficacy = luminous flux emitted by the light source (lumens)/ light source power (watts). Its unit is lm/W. For two lamps with the same power, the one that emits a higher luminous flux has a higher luminous efficacy.
Luminous efficacy vs. luminous efficiency
The two words luminous efficiency and luminous efficacy are very similar, and many people often use them to replace each other. In fact, these two concept both measure the ability of the light source to convert electricity into visible light, but their calculation methods are different. Luminous efficiency is the ratio of the luminous flux of the light source at 1 W to the maximum luminous flux that the human eye can perceive at 1 W. It is a percentage and has no unit. The maximum visible light flux of a 1W lamp is 683 lumens, emitted by 555 nm green light, because the human eye is most sensitive to green light.
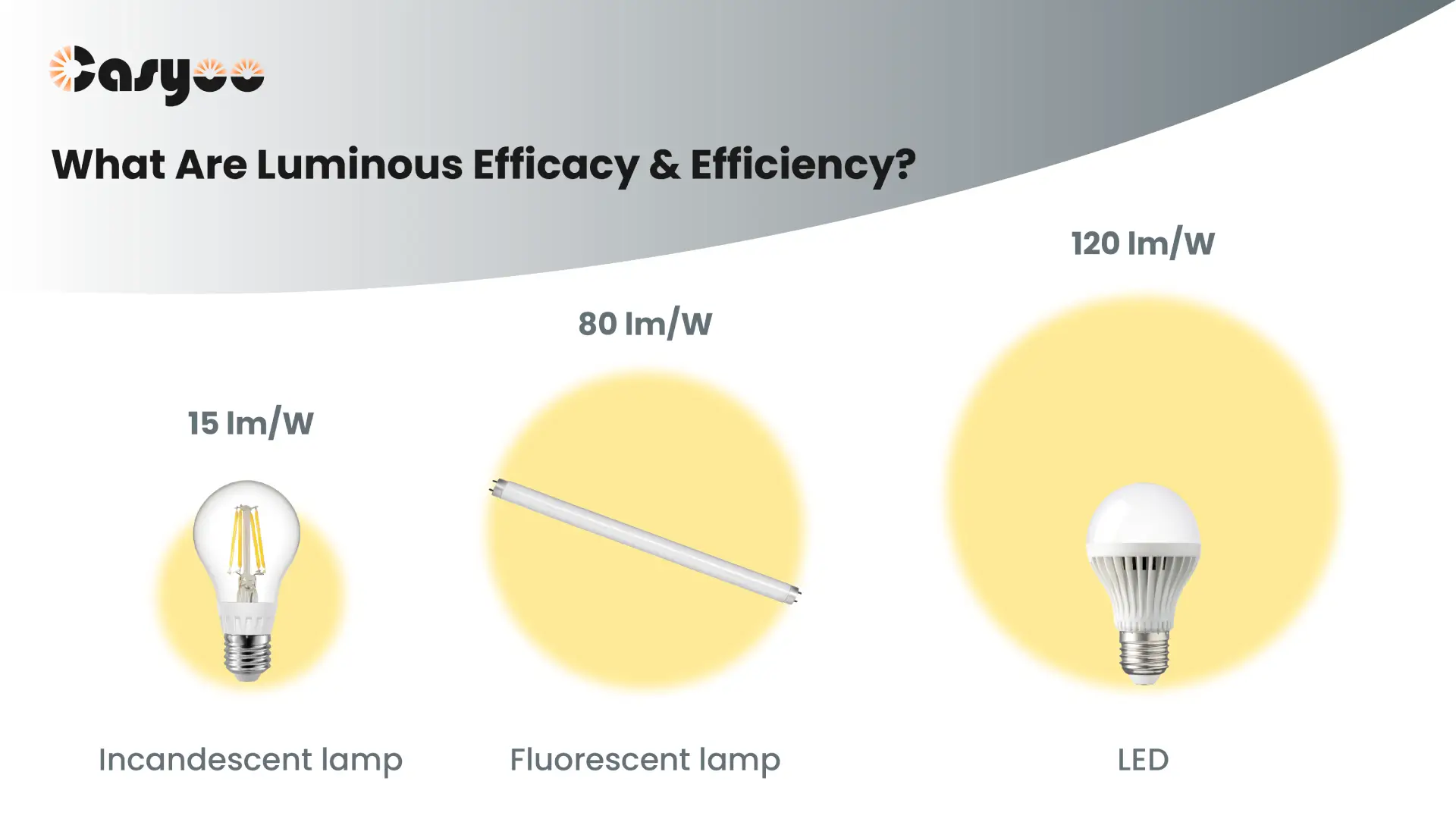
Luminous efficacy of different light sources
Incandescent lamps
Since incandescent lamps heat tungsten filaments to generate heat and then emit light, heat is the main product while light is a byproduct. Therefore, their luminous efficacy is particularly low, which can only reach 7-15 lm/W.
Halogen lamps
In order to improve the efficacy of incandescent lamps and extend their lifespan, people have invented halogen tungsten lamps. The efficacy of halogen tungsten lamps is higher than that of incandescent lamps, at 15-25 lm/W.
Fluorescent lamps
Fluorescent lamps no longer emit light by heating tungsten filaments, but through exciting the atoms to emit ultraviolet rays, and then excite phosphors to emit visible light. In this way, more energy is converted into light instead of heat. The efficacy of fluorescent lamps is 5-8 times higher than that of incandescent lamps, which is generally more than 80 lm/W, and some can reach 110 lm/W. Fluorescent lamps need to be equipped with ballasts to work properly, which also need a certain power. When we calculate the efficacy of fluorescent lamps, the power should be the total power of the lamp tube and the ballast.
HID lamps
High-intensity gas discharge lamps (HID), like fluorescent lamps, emit light through gas discharge, but their gas discharge process is of high-intensity. Metal halide lamps, as a type of the HID lamps, excite various metals inside to emit light. They also need triggers and ballasts. The efficacy of HID lamps is also relatively high, reaching 70-110lm/W.
LED lights
The luminous materials of LEDs are semiconductor, and common ones include gallium nitride (GaN) and aluminum gallium phosphide (AIInGaP). These materials have narrow band gaps and can achieve efficient conversion of electrical energy into light energy. The substrate materials are generally sapphire (sapphire) or silicon carbide (SiC), which have good light transmittance, which improves the efficacy of LEDs. In addition, since LED lights use solid materials to emit light, they generates less heat than thermal radiation and gas discharge. The majority of the electrical energy is transformed into light energy. The efficacy of LED lamps is about 80-130 lm/W, and it is still improving.
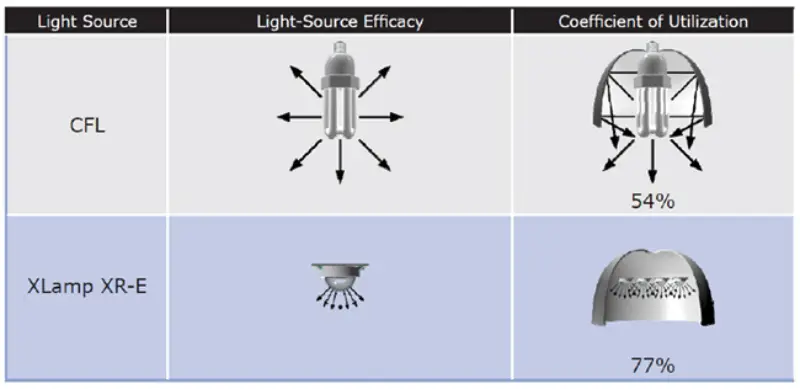
Utilization coefficient: measurement of lamp efficiency
There is another concept related to luminous efficacy, the utilization coefficient of lamps. The utilization coefficient of lamps is the ratio of effective light output to the total light output of the lamp light source. Light bulbs work in the lamps, and the reflectors, lenses, and shades of the lamp will cause light loss. In addition, some light sources like the CFL lights emit diffuse light that shine in all directions, and a lot of light is wasted. The actual efficacy of LEDs is high, because they have optical designs, which make the light emit in a specific direction.
How to improve luminous efficacy?
There are many factors that affect the luminous efficacy, and by analyzing them and carrying out corresponding solutions, experts can improve the efficacy of LED lights. We will discuss several of the solutions in the following paragraphs.
- Junction temperature
LED converts electrical energy into light energy by forming a PN junction, and the temperature of the PN junction is called the junction temperature. Simply put, the junction temperature is the temperature of the LED chip. As the junction temperature rises, LED luminous efficacy falls. Therefore, when designing a high-current LED that can provide high-lumen light, the influence of temperature must be considered at the same time. The current methods used include reducing the thermal impedance of the chip, the thermal impedance of the control module and the board, and improving the heat dissipation of the chip.
- Chip
By expanding the luminous area of a single LED wafer or combining several LED wafers together, the luminous efficacy of the LED chip can be improved. What is important is to balance the increase in brightness and heat dissipation.
- Package structure
A reasonable package structure is conducive to the emission of light and can improve the luminous efficacy of the LED light. Selecting the appropriate shape, depth, and angle of the reflector cup helps minimize the loss of light.
Conclusion
The concept of luminous efficacy provides a unified standard for comparing how efficient are different lamps. From incandescent lamps to LED lamps, the luminous efficacy of lamps has been continuously improved. This article also introduces the concepts that are similar to luminous efficacy: luminous efficiency and lamp utilization coefficient. In the future, by optimizing various aspects of LED lamps, the luminous efficacy of LED lights will continue to improve. Read Casyoo Blog to get more professional knowledge on LED lamps!