Is it true that LED lights don’t produce heat? The answer is no. Even though they are known as the cold light source, that doesn’t mean that they don’t produce heat at all. However, comparing with other light sources, they are truely much more cooler while working. What to know why do they generate relatively less heat and how to make your LED lights emit as little heat as possible? Keep reading on!
Do LED lights get hot?
Yes. LED lights produce heat by non-radiative recombination. In a diode like LED light, the electron-hole pairs recombine at the pn junction and release energy through energy level transition. The lamp glows as the radiative recombination’s excess energy emit photons. Heat is one of the other energy-releasing products of non-radiative recombination. Internal quantum yield can be defined as radiative recombination divided by total recombination rate. Heat generation decreases with increasing internal quantum efficiency. Furthermore, only by means of rectification, filtering, buck-boost, dimming, and other circuits can the LED chip be connected to the 220V voltage. These circuits will also generate heat.
How hot is too hot for LED lights?
Generally speaking, the operating temperature of LED lamp beads should be below 65°C-80°C to ensure long-term stability and extend their service life. For high-power LED lamp chips, their operating temperature may be higher than this, and the temperature of the heat sink can sometimes reach around 100°C. It is worth noting that the actual operating temperature of LED lamp beads is affected by many factors, including the power, the heat dissipation technology used (such as the design and efficiency of the heat sink), ambient temperature, and airflow conditions.
Which produce more heat: LED vs traditional lamps
LED lighting generates less heat than traditional lights. LEDs emit mainly visible light with wavelengths between 380 and 780 nanometers. They are cold light sources. In contrast, traditional xenon lamps, halogen lamps, and incandescent lamps are thermal light sources, and a large part of their energy is converted into invisible infrared light when they emit light. Heat is conducted by infrared light. Bathroom heaters, for example, use infrared rays to conduct heat. This type of thermal light sources are therefore very inefficient. If they want to achieve the same brightness as LED lamps, they have to apply a higher wattage, which will generate more heat. High-power halogen lamps can even reach temperatures of several hundred degrees.
Furthermore, LED manufacturers place a high value on heat dissipation when designing LED lamps, because if heat cannot be dispersed, the chip’s luminous efficiency suffers. Therefore, LED lamps generally have heat sinks and other design for heat dissipation.
Do LEDs get hot enough to start a fire?
The possibility of LED lamps causing fire is very small. If the lamp is overheated, the chip itself will break down first, causing an open circuit. Basically, as long as the driver power supply is compliant, there is no danger of causing fire. The only danger is that if you use a non-isolated driver power supply, it may cause electric shock.
In addition, since the LED lights generate little heat and have a reasonable heat dissipation design, the heat it generates cannot reach the ignition point of the plastic shell of the lamp. However, we should also consider the using environment of LED lights. A fire could start if the surrounding temperature is too high. Before you buy the light, you should look for the working temperature of the LED lights to make sure they can work in your area.
How to choose LED lights that emit little heat?
First of all, it is necessary to choose LED chips with high efficiency, so that it requires lower wattage to achieve the same brightness, and generates less heat.
You should also think about how reasonable the lights’ heat dissipation design is. Common heat dissipation methods are generally divided into two categories. The first is to choose suitable materials. Substrate materials, adhesive materials, and packaging materials are the three general categories of materials. When it comes to substrate materials, they should have a chip-matching thermal expansion coefficient, high electrical insulation, high stability, and high thermal conductivity. The most often utilized substrate materials are silicon, composite materials, metal (copper, aluminum, etc.), and ceramics (A1N, SiC).
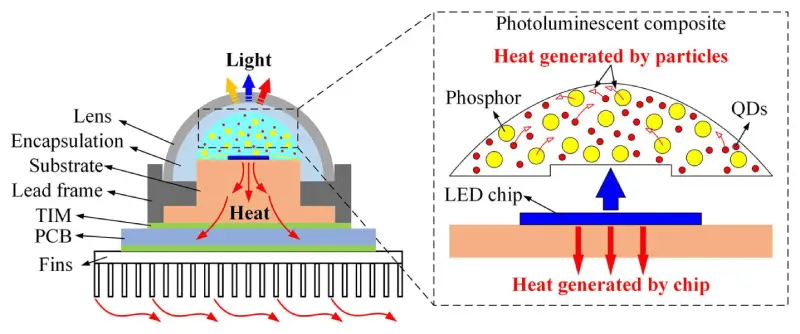
The second is to improve heat dissipation system, which is primarily split into passive and active forms, in the process of transferring heat from the package substrate to the external heat sink. The term “active heat dissipation” describes using a heat dissipation mechanism to lower the LED lamp’s temperature. It mainly includes the installation of fan, liquid cooling system, semiconductor refrigeration system, ion wind system and synthetic jet system. Passive heat dissipation refers to dissipating the heat generated during LED lighting through the radiator itself. Heat dissipation is classified into two types: direct natural convection and heat pipe (flat, loop, and finned) technology heat dissipation.
3 tips for keeping LED lights cool
1. How can I prevent the overheating of my LED lights?
- Dust collection can hinder heat dissipation, therefore keep the lights clean and maintained on a regular basis.
- Avoid long-term continuous use of LED lamps.
- Add structures such as heat sinks and heat dissipation fins to increase heat dissipation area.
- Select materials with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum alloy and copper.
- Select efficient drive circuits to reduce energy loss and heat generation.
- Use constant current driver. Constant current driver can ensure the stability of the working current of LED lamps and reduce the impact of current fluctuations on lamps.
- Control the brightness of LED lamps. Appropriately reducing the brightness can reduce the heat.
- Add fans or heat dissipation ducts to reduce the temperature of lamps.
- Use heat dissipation glue or heat dissipation silicone grease to increase the contact between the lamp and the radiator and improve the heat dissipation effect.
2. Can I keep LED lights on all night?
Generally speaking, high-quality LED lights last for more than 15,000 hours. When used for eight hours per day, they can last three to five years. In addition, LED lights generally has a good heat dissipation design, so it is okay to leave LED lights on all night. If your lamp becomes very hot after working for a long time, then you should avoid using it for a long time to prevent causing damage to the lamp. Excessive heat will cause the lamp beads to age, and the brightness of the lamp will be significantly worse over time. This is light decay. For high-quality LED lamps, at the end of their service life, they can still maintain about 80% of the originally brightness. For lamps of poor quality, their brightness may be lower in 3-5 years.
3. What is the appropriate working temperature of LED lights?
The working temperature LED lamps is generally designed to be between -20℃ and 40℃. For cold regions, the operating temperature of lamps must be designed to be between -40℃ and 40℃ to meet the use requirements. The summer temperature in the equatorial region may reach 50℃ or higher, so the operating temperature of lamps is around 0℃-50℃. In areas with extreme temperatures, LED lamps should be equipped with corresponding low-temperature or high-temperature resistant devices.
Conclusion
LED lights will get hot because not all of the electricity can be transform into light, and part of the energy will turn into heat. But they produce less heat than traditional lamps, and they are not likely to cause fire. It is necessary to choose high-quality LED lights with reasonable heat dissipation design. Casyoo applies the most reliable technology to design the heat dissipation system of our lights, and our LED lights have passed related tests. Contact us to get safe LED lights that produce little heat!




