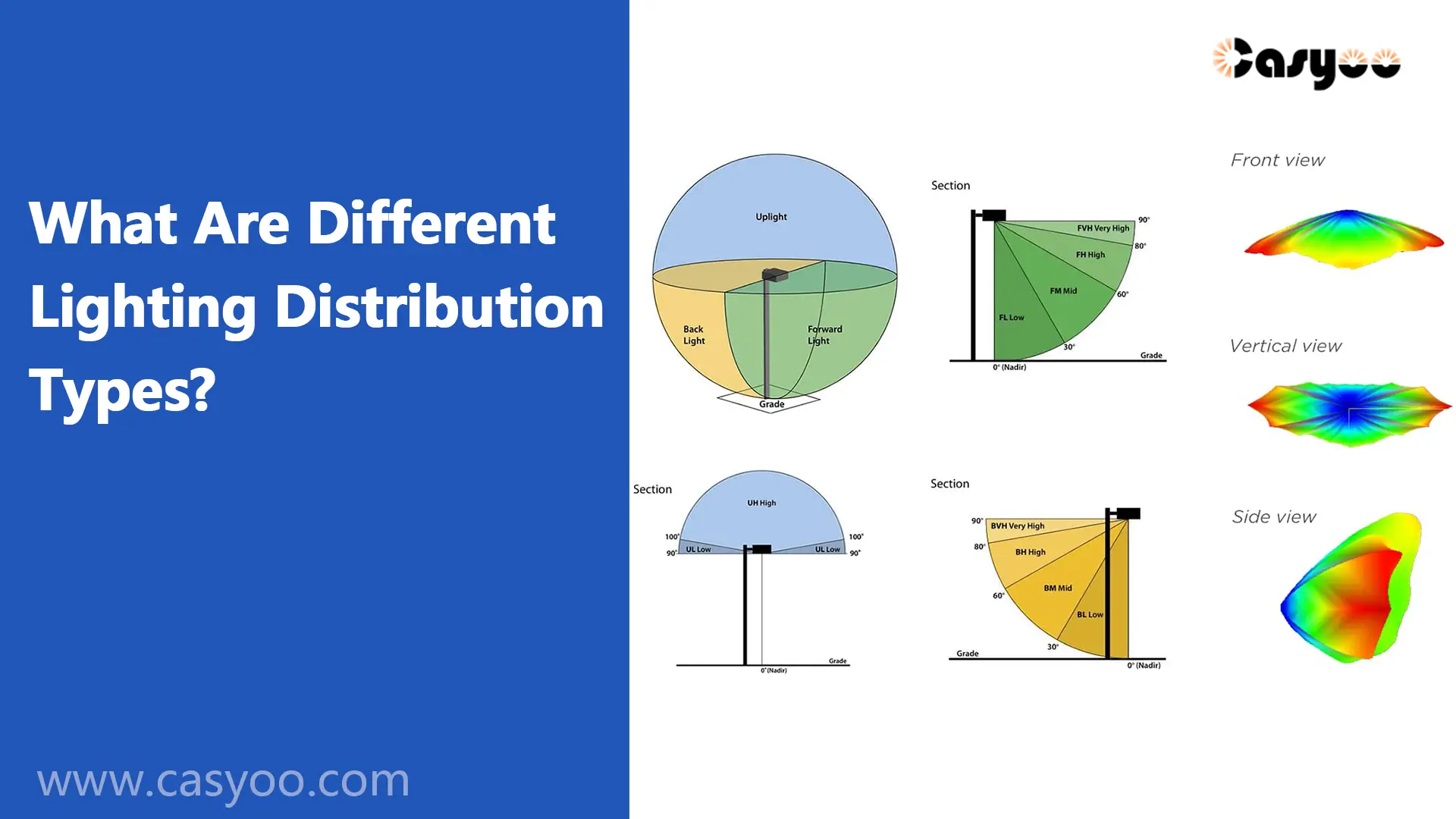
The light distribution is the intensity of light that a source emits in all directions. For LED street lights, proper light distribution is essential to ensure that all emitted light is efficiently utilized on the illuminated road surface. This is necessary to meet road lighting requirements. Here, we introduce the two most authoritative standards from IESNA and NEMA about lighting distribution types.
What are the IESNA 5 types of lighting distribution?
In the IESNA standard, the light distribution of street lights is categorized into five types:
- Type I: Primarily used for narrow sidewalks or bicycle lanes. The lamp head situated in the center of the road. The lighting width is similar to the lamp height.
- Type II: Mainly for wider sidewalks, entrances to traffic lanes, or other long and narrow lighting applications. The light head is located on one side of the road, with the lighting width approximately 1.75 times the lamp height.
- Type III: Commonly used for highways, driveways, parking lots, and general square lighting. The lamp head is positioned on the roadside, with the lighting width 2.75 times the lamp height.
- Type IV: Typically for wall washing and large-scale parking lots, with a light pattern similar to a semicircle.
- Type V: Used for general parking lots and large-scale square lighting, with the lighting range forming a circle and the lamp head located in the center of the lighting area.
LED street lights primarily utilize three types of light distribution designs: Type I, Type II, and Type III, chosen according to the specific road type. Generally, the original light emission angle and intensity distribution of LED lights may not meet the requirements of a specific scene, so secondary light distribution is essential. One way is to disperses light to form a larger angle, creating a more uniform light spot. Another way is to concentrates light into a smaller range to increase the central luminous intensity. The light distribution of Casyoo LED lights is well designed, and can fit various applications.



NEMA beam angle and light distribution
NEMA outlines seven types of light distribution, each representing a specific beam angle, beam width, and projection distance as the following table.
| Type | Beam Angle | Beam Width | Projection Distance |
| 1 | 10-18 | Very Narrow | >72 |
| 2 | 18-29 | Medium Narrow | 60-72 |
| 3 | 29-46 | Narrow | 52-60 |
| 4 | 46-70 | Medium | 43-52 |
| 5 | 70-100 | Medium Wide | 32-43 |
| 6 | 100-130 | Wide | 24-32 |
| 7 | >130 | Very Wide | <24 |
The categories describe the distribution of light from both horizontal and vertical directions. For instance, a light with a horizontal angle of 80 and a vertical angle of 120 corresponds to NEMA 5×7.
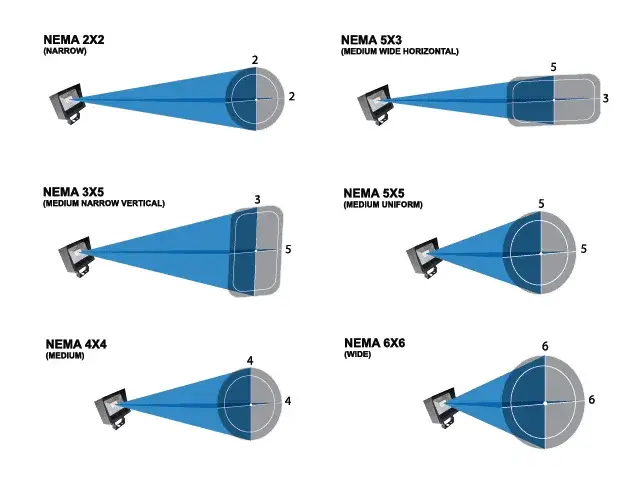
Common beam angles include:
- NEMA III/NEMA IV: These provide a circular light distribution with a relatively small beam angle. They are suitable for small sports fields, and high bay lights also apply these types.
- NEMA 5×3: This type offers a rectangular shape of light distribution commonly used in street lighting. Its shape resembles the roads, minimizing energy waste.
- NEMA V: This type provides a wider circular light distribution and is suitable for larger spaces, such as warehouses.
- NEMA VI: Some flood lights use this light distribution type for wider illumination. This design makes them suitable for garden lighting, architecture lighting, and similar applications.
Conclusions
In conclusion, different LED lights feature distinct light distribution designs. Understanding these variations is crucial for selecting the right lighting solution. Adhering to the standards set by IESNA and NEMA ensures the appropriate selection of LED lights that provide sufficient illumination without energy waste. It is wise to consult an experienced LED manufacturer like Casyoo to get the specific lighting design for your space.