Photometry studies the intensity, brightness, color, spectral distribution, and other characteristics of light. It involves the propagation, absorption, reflection, refraction, scattering, and other phenomena of light. By studying the characteristics of light, we can design a lighting system that meets human needs. In a lighting project, designers will make use of the knowledge and experience in the photometric study to consider the brightness, color temperature, illumination, and other parameters of the light source, so as to achieve energy-saving, comfort, and aesthetic lighting. Let’s get to know more about the photometry study that helps provide perfect lighting!
What parameters does photometric study focus on?
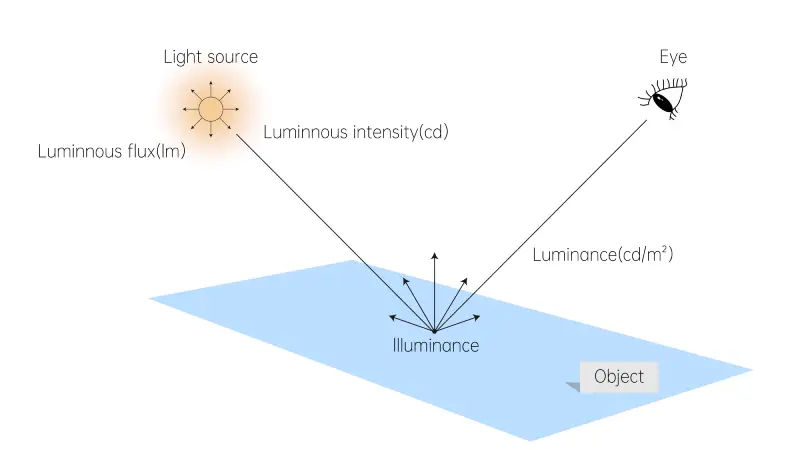
- Luminous flux: The amount of energy perceived as light that a light source radiates to its surroundings in a certain amount of time is referred to as luminary flux. The standard symbol for it is ø, and the unit is “lumen (lm)”.We can say that the total amount of light output by a bulb is its luminous flux.
- Luminous intensity: The fundamental unit of photometric measurement is luminance. It refers to the distribution of luminous flux of a light source in a given direction, that is, the spatial distribution density of luminous flux. Its unit is “candela (cd)”.
- Illuminance: It is the amount of light flux received per unit area of the illuminated surface. Its primary purpose is to show how intense the illumination is on the illuminated surface. It can be determined by dividing the luminous flux by the area. Its symbol is E and the unit is “lux (lx)”.
- Luminance: Luminance is the parameter that measures how we perceive the light, which is, how bright we think the light is. The unit is “candela/square meter (cd/㎡)” and the symbol is L.
- UGR: The Unified Glare Rating (UGR) is an indicator that measures glare and evaluates how comfortable an individual is with the light. The numbers that represent UGR range from 10 to 30. The majority of individuals will be uncomfortable with a more direct glare the higher the number. For instance, UGR 19 indicates that while 35% of those in the room will experience light-related discomfort, 65% of them do not actually experience any interference from the glare.
- Besides the above four main parameters of light, we also consider color temperature, which decides the hue of white light; CRI, which determines how clearly the light source can display the objects’colors, and so on.
Importance of photometric study in lighting
The cost of lighting design based on a photometry study can be even higher than the price of your lights. But if you choose to purchase lights from manufacturers like Casyoo, the design is usually included in the whole plan. Only when combined with reasonable photometry design can your lamp achieve the best lighting. Some of the importance of photometry study in lighting include:
- Functionality: For indoor lighting, lights in different areas play different roles. In areas with high traffic, such as the living room, high brightness and uniform lighting are required. In the reading and learning areas in the study room, it is necessary to arrange the lights for task lighting.
- Appropriate lighting: Reasonable photometric design can avoid some negative influences of unsuitable lighting, such as glare, alternating light and dark areas, and inappropriate brightness. For example, if the lighting in the office space is too dark, it can easily lead to reduced office efficiency. If the brightness is set too high, it can cause glare and discomfort.
- Considering psychological effects: In spaces such as bedrooms and bathrooms, for the privacy and psychological security of the space, designers tend to create comfortable, natural, and low-brightness lighting. For road lighting, it is necessary to make the lighting bright and clear enough to keep the drivers
Procedures of photometric study in lighting
- Analyze functions of lighting: Understand the role of lighting in a specific environment by focusing on the functions of the space and people’s needs.
- Determine parameters and their values: Consider the required lighting standards to set the reasonable values of each parameter.
- Select lighting control systems: Pick the right control systems to provide precise and variable lighting.
- Select luminaire types: Decide on the type, quantity,and location of luminaires.
- Integrate and optimize: Take into account every aspect collectively, as well as the effects of both artificial and natural light.
Example 1: photometric study in parking lot lighting
1. Analyse illumination standards
Take China’s parking lot standards as an example. According to the Outdoor Work Site Lighting Design Standard and the Urban Road Lighting Design Standard, the horizontal illumination standard for parking lots with more than 400 parking spaces is 30 lx, and the illumination uniformity must reach 0.25 or above. The average horizontal illumination required for general parking lots with high traffic is 20 lx, and the illumination uniformity must reach 0.25 or above. There should be at least 50 lx of illumination at the parking lot’s entrance and exit. At the entrance and exit, clear lighting can ensure safety and facilitate document inspection, driver identification, and other tasks. In addition, it is necessary to reduce light pollution to the surrounding environment through reasonable arrangements of lamps.
2. Consider the lighting requirements
Illuminance uniformity, light source color rendering, color temperature, and glare are all important considerations for measuring the quality of lighting. High-quality lighting can provide a comfortable visual environment for drivers and pedestrians.
3. Arrangement of the lamps
Choose single-head street lamps with a lower height and semi-cutoff design, and arrange certain numbers of lamps to improve illumination uniformity and prevent light pollution. The installation height of lamps is generally 8 meters, and the spacing is around 25 meters.
4. Lamp selection
At the parking lots, effective LED lamps are the best choice. The light output rate of these lamps should be more than 85%, with a power factor of more than 0.95, a light efficiency of more than 100 lm/W, a color temperature of 4000K-4500K, a color rendering index Ra≥80, a service life of more than 30,000 hours, and an IP65 waterproof rating.
5. Lighting control system
We will apply light control, time control, and manual control for the lights. The light control components control the switch according to the natural light illumination, and the timer can achieve precise control of the of the longitude and latitude clock controller.
6. Illuminance calculation:
Use DIALux to simulate and calculate the illumination, and the results show:
Average illumination: 31 lx (> standard 30lx)
Minimum illumination: 25 lx
Maximum illumination: 36 lx
Illuminance uniformity=minimum illumination/average illumination=0.812 (> standard 0.25)
As the result meets the corresponding standards and requirements, the above can be a feasible lighting scheme.
Example 2: photometric study in commercial lighting
Take the office building lighting as an instant, and the procedures will be like:
- Determine important factors
- Illumination: Usually, the illumination in the collective office area is not less than 300 lx.
- Illumination uniformity: The uniformity of light should be as close to 1 as possible to improve comfort.
- Preventing glare: If the brightness is too high or the brightness contrast is too obvious, it will cause glare and affect visual comfort. By setting suitable brightness, increasing ambient light brightness, and choosing lamps with reasonable lighting distribution design, we can keep the glare under control.
- Color temperature: Use a 4000-5500K color temperature similar to daylight to improve work efficiency.
- CRI: Choose a CRI of Ra>80 to ensure visual accuracy, especially for the office environments of precise work.
- Control method: In order to achieve the purpose of energy saving, motion sensors are often installed in lamps to achieve intelligent lighting that turns off the lights when people leave.
- Lamp installation: The shading angle of the lamp should be greater than 30 degrees to prevent light from illuminating all directions. Another way to shade the diffused light is to raise the light source’s installation height.
- Different plans for different places:
- Comprehensive office area
| Area | Lux level | Max UGR | Emin/Eavg | Ra |
| Lobby | 300-500 | 19 | 0.4 | 80 |
| Reception desk | 500-800 | 19 | 0.4 | 80 |
- Public office area
| Area | Lux level | Max UGR | Emin/Eavg | Ra |
| Office area | 300-500 | 19 | 0.6 | 80 |
- Independent office
| Area | Lux level | Max UGR | Emin/Eavg | Ra |
| Desktop | 300-500 | / | 0.6 | 80 |
| Reception desk | 150-200 | 19 | / | 80 |
- Meeting room: the main lighting is concentrated on the conference table, with auxiliary lighting around it.
| Area | Lux level | Max UGR | Emin/Eavg | Ra |
| Office area | 300-500 | 19 | 0.6 | 80 |
Conclusions
This passage provides a brief introduction to the photometry study used in the field of lighting. Getting to know the considerations, importance, procedures, and examples of the photometry study must have made you realize how much you need it for your project. Then contact us to discuss more about your project and let us provide a professional solution as well as satisfying lights!